Please peruse our frequently asked questions to address any concerns that you may have. Simply click to expand. If you don’t find a solution to your question, please contact one of our helpful associates who would be happy to assist.
Kids Feet - Frequently Asked Questions
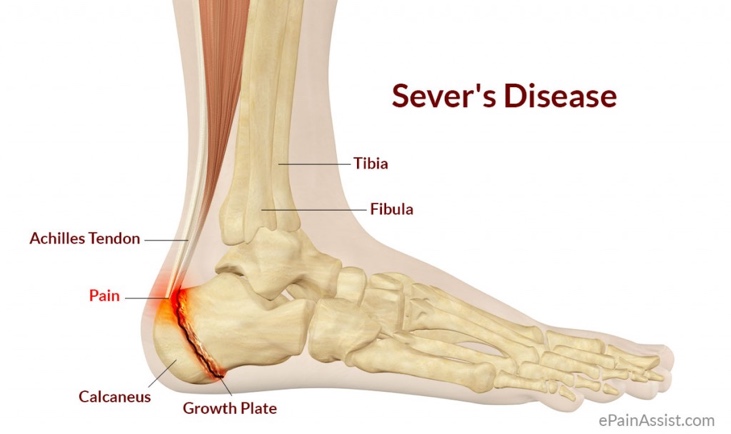
Sever's Disease
WHAT IS IT?
Heel pain associated with growth spurts. This occurs usually from repetitive stress on the growth plate on the heel from the calf muscles/Achilles tendon pulling too hard. It is a growing pain.
WHAT CAUSES IT?
Growth spurts and/or increased activity levels. Common found with active children who play sports such as soccer, basketball, running. Tight calves can also cause issues as will poor biomechanics. It is more common in males than females.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS?
Heel pain, calf pain, discomfort with and after activity (after the car ride home and stepping down), limping.
TREATMENT?
Sever’s Disease usually resolves itself after growth spurts. You can also rest, apply ice, do calf stretches, wear supportive/cushion footwear, use custom made or over the counter orthotic devices, wear night splints.
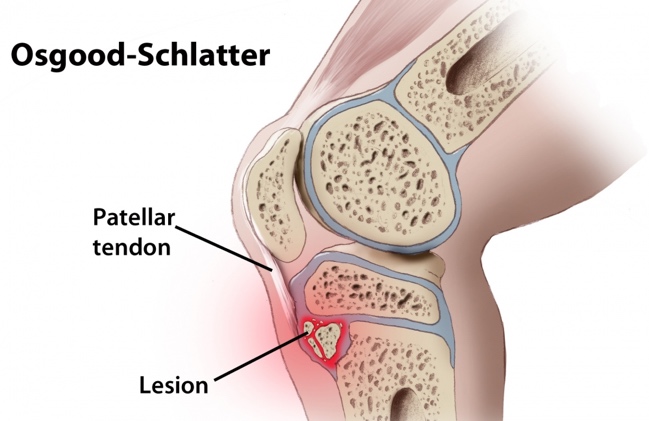
Osgood Schlatter Disease
WHAT IS IT?
Knee/under knee pain associated with growth spurts. Usually caused from the quadriceps muscles pulling on the growth plate on the tibial tubercle creating pain and a bone growth. It is a common growing pain.
WHAT CAUSES IT?
Tight quadriceps muscles (during growth spurts, bones grow faster than muscles). Active children may experience this especially is participating in jumping and running sports (volleyball, basketball).
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS?
Pain at the knee and below the knee. Bone growth/bump below the knee. Pain is associated with or without activity. Symptoms include swelling and limping.
TREATMENT?
Usually resolves after growth spurt. Rest, decreased activity, icing, NSAIDS, Patella/knee brace, stretching, laser, supportive footwear and custom made or over the counter orthotic devices will help.
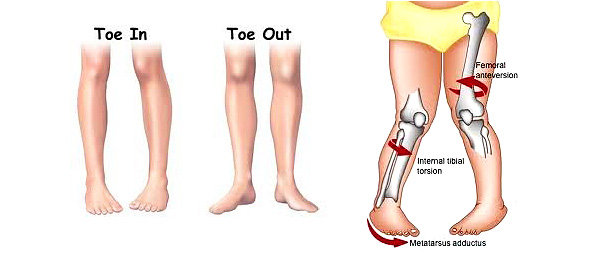
Intoeing
WHAT IS IT?
Feet will be turned in as the child walks. Usually normal until the age of 6-7 years old as the child’s bones will continue to unwind and grow from the fetal position, but if it continues after the age of 7, this is not normal.
WHAT CAUSES IT?
Hereditary/Genetic conditions. Ligament laxity. Sitting and sleeping habits. Failure of the bones to unwind (hip, upper leg bone, lower leg bone, feet bones).
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS?
Sitting in the “W” position. Feet turned in as they walk. Difficulty walking/running. Tripping, balance issues. Tight calves/pain. Knees facing each other when feet are facing straight. Lower leg fatigue.
TREATMENT?
– Monitor/Wait to see if it corrects itself
– Support footwear/modified footwear
– Custom made or over the counter orthotic devices (Gait Plates)
– Passive Stretching/casts
– Physical Therapy/roller blading
– Braces/night splints
– Avoid sitting in “W” position and change sleeping patterns
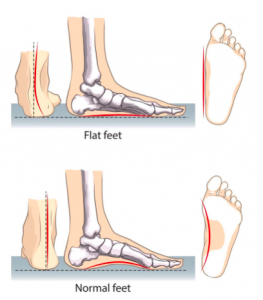
Flat Feet
WHAT IS IT?
The arch of the foot is lowered, flattened or non-existent. This can be normal until the age of 7 as the child is still growing and developing. Usually child feet are very hypermobile.
WHAT CAUSES IT?
– Hereditary/genetic conditions
– Hypermobile joints
– Ligament laxity
– In-toe gait
– Extra bone growth
– Coalition (2 bones are fused together)
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS?
Flattened arch. Ankles sticking out. Foot, ankle, knee, hip or back pain. Fatigue easily. Difficulty walking/running. Tight calf muscles
TREATMENT?
– Monitor/Wait to see if grow out of it
– Custom made or over the counter orthotic devices
– Supportive/modified footwear
– Stretching
– Exercises
– Surgery (Genetic conditions)